Reaction Of Nh3 And Hcl
Place full-bodied ammonia solution on a pad in one cease of a tube and concentrated hydrochloric acid on a pad at the other and sentry every bit the two gases diffuse far enough to meet and grade a band of solid ammonium chloride
This demonstration is best performed in a fume cupboard. A black background, such every bit a sheet of black carbohydrate paper, behind the demonstration helps the white ring to be seen more clearly. Actually performing the demonstration takes only a few minutes.
Equipment
Appliance
- Eye protection (goggles)
- Access to a smoke cupboard
- Protective gloves (preferably nitrile)
- A length of glass tube about half a metre long with an inside diameter of near 2 cm (note i)
- Retort stands with bosses and clamps x2
- Modest wads of cotton wool wool x2
- Bungs x2 (to fit into the ends of the glass tube)
- Strip of universal indicator paper (optional)
Chemicals
- Full-bodied hydrochloric acid (CORROSIVE), a few cmthree (note 2)
- 880 ammonia solution (CORROSIVE, Unsafe FOR THE ENVIRONMENT), a few cmiii(note 2)
- Acetone (Flammable), a few cmthree (optional, note 1)
Equipment notes
- It is very important that the tube is make clean and completely dry for this experiment. If necessary, the tube can be dried by pushing a cotton wool pad soaked in acteone through the tube and leaving it for a few minutes.
- The concentrated muriatic acid and the 880 ammonia solution are easier to handle in small bottles than in Winchesters (big bottles) for this demonstration.
Wellness, prophylactic and technical notes
- Read our standard wellness and safety guidance
- The demonstrator should wear goggles and protective gloves.
- Concentrated hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq), (CORROSIVE) – see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC047a. Produces hydrogen chloride gas, HCl(yard), (TOXIC, CORROSIVE) – see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC049.
- 880 ammonia solution, NH3(aq), (CORROSIVE, DANGEROUS FOR THE Surroundings) – see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC006. Produces ammonia gas, NH3(g), (TOXIC) – see CLEAPSS Hazcard HC005. Care should be taken when opening the canteen of ammonia solution, specially on hot days when pressure level can build up in the bottle. If the bottle of ammonia is kept for a long fourth dimension, its concentration may decrease which volition lessen the effectiveness of the sit-in.
Procedure
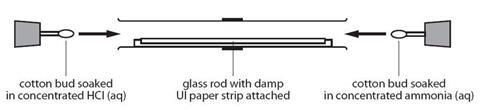
- Working in the fume cupboard, clench the glass tube at either end, ensuring that it is horizontal.
- Open the bottle of ammonia solution charily, pointing the bottle abroad from both yous and the audition. Open up the bottle of hydrochloric acid and concord the stopper well-nigh the mouth of the ammonia bottle. Annotation the white clouds of ammonium chloride that form.
- Put one of the cotton wool wads in the oral fissure of the ammonia bottle and carefully invert it to soak one side of it. Push the soaked end into one cease of the glass tube. Replace the lid on the bottle.
- Repeat this procedure quickly with a second wad of cotton wool and hydrochloric acid. Put the cotton wad into the other end of the drinking glass tube.
- Putting bungs into the ends of the glass tube will reduce the quantity of the gases which escape and therefore the odor. Once assembled, the tube can be removed from the fume closet.
- Sentry the tube and discover a ring of white powder forming nigh the middle of the tube. This is ammonium chloride.
Teaching notes
The reaction which is taking place is:
ammonia + hydrogen chloride → ammonium chloride
NH3 (g) + HCl (g) → NH4Cl (s)
It typically takes only a few minutes for the ring to form, only the verbal time will depend on the dimensions of the tube, the amount of the solutions which are put on the cotton wool wads and the temperature of the room.
The ring ordinarily forms nearer to the muriatic acid end of the tube because hydrogen chloride diffuses more slowly than ammonia. This is considering hydrogen chloride has nigh twice the molecular weight of ammonia, and the rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the molecular mass of the gas.
It is worth noting that the rate of diffusion is non the same equally the speed at which the gas molecules travel (which is hundreds of meters per second). The gas molecules follow a zig-zag path through the tube as they collide with the air molecules in the tube.
The purpose of the glass tube is to eliminate air currents and to see if the gas molecules will move on their ain.
Boosted information
This is a resource from the Practical Chemistry project, developed by the Nuffield Foundation and the Royal Order of Chemistry. This collection of over 200 practical activities demonstrates a broad range of chemical concepts and processes. Each activeness contains comprehensive information for teachers and technicians, including full technical notes and step-by-step procedures. Practical Chemistry activities accompany Applied Physics and Applied Biology.
© Nuffield Foundation and the Majestic Society of Chemistry
Health & Condom checked, 2016
Reaction Of Nh3 And Hcl,
Source: https://edu.rsc.org/experiments/diffusion-of-gases-ammonia-and-hydrogen-chloride/682.article
Posted by: moratrailtandes.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Reaction Of Nh3 And Hcl"
Post a Comment